While pipes and tubes may look similar, they are designed for different purposes and have distinct characteristics. Here’s a breakdown of their differences:
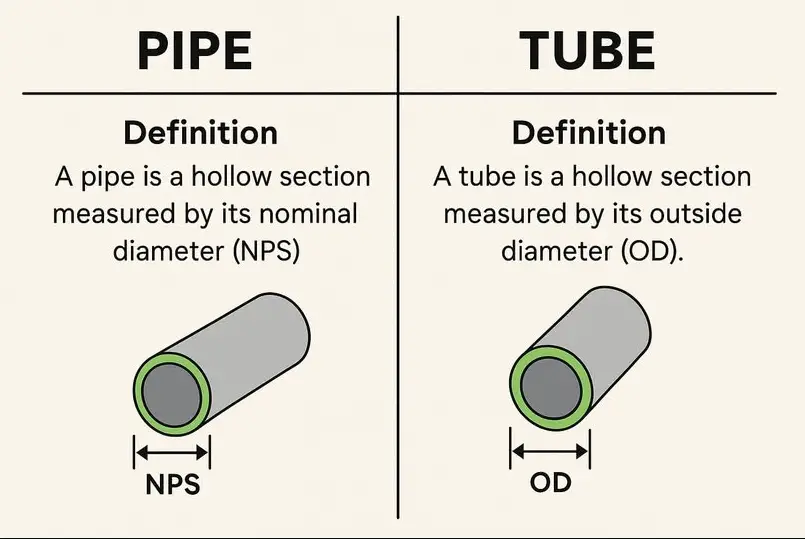
1. Primary Purpose
| Feature | Pipe | Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Main Use | Transport fluids/gases (e.g., water, oil, gas) | Structural applications (e.g., frames, machinery, heat exchangers) |
| Pressure Handling | Designed for high-pressure systems | Typically used for low-pressure applications |
| Standardization | Follows Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) and schedules (e.g., SCH 40, SCH 80) | Measured by outside diameter (OD) & wall thickness (e.g., 1″ OD, 0.065″ wall) |
2. Size & Dimensions
| Feature | Pipe | Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Size Reference | Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) – Approximate ID (not exact) | Actual Outside Diameter (OD) – Precise measurement |
| Wall Thickness | Defined by schedule (e.g., SCH 40, SCH 80) | Measured directly (e.g., 0.125″, 2mm) |
| Tolerances | Looser tolerances (focus on pressure rating) | Tighter tolerances (precision applications) |
Example:
-
A 1″ Schedule 40 Pipe has:
-
Outside Diameter (OD) = 1.315″
-
Inside Diameter (ID) ≈ 1.049″
-
-
A 1″ Tube has:
-
OD = Exactly 1.0″
-
Wall thickness varies (e.g., 0.065″, 0.083″)
-
3. Shape & Flexibility
| Feature | Pipe | Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Mostly round (some square/rectangular for structural use) | Round, square, rectangular, oval |
| Flexibility | Rigid, designed for fixed installations | Can be more flexible (e.g., hydraulic tubes) |
4. Material & Manufacturing
| Feature | Pipe | Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Carbon steel, stainless steel, PVC, CPVC | Steel, aluminum, copper, brass, titanium |
| Production | Made for large-scale fluid transport | Made for precision applications (e.g., medical, aerospace) |
| Surface Finish | Rough (often coated for corrosion resistance) | Smooth (polished for aesthetics/functionality) |
5. Connection Methods
| Feature | Pipe | Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Joining | Welded, threaded, flanged | Welded, brazed, compression fittings, flared ends |
| Fittings | NPT (National Pipe Thread), socket weld | Ferrule fittings, push-to-connect |
6. Applications
Common Uses of Pipes:
-
Water supply lines
-
Oil & gas pipelines
-
Plumbing & HVAC systems
-
Industrial process piping
Common Uses of Tubes:
-
Structural frameworks (e.g., handrails, scaffolding)
-
Hydraulic & pneumatic systems
-
Heat exchangers & condensers
-
Automotive & aerospace components
Quick Summary Table
| Aspect | Pipe | Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Fluid/gas transport | Structural/precision uses |
| Size Reference | Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Exact OD & wall thickness |
| Shape | Mostly round | Round, square, rectangular |
| Tolerances | Looser | Tighter |
| Pressure Handling | High | Low-medium |
| Joining Method | Threaded, welded, flanged | Compression, brazing, welding |
When to Use Pipe vs. Tube?
-
Use Pipes for: Plumbing, oil/gas, high-pressure systems.
-
Use Tubes for: Structural support, machinery, precision applications.