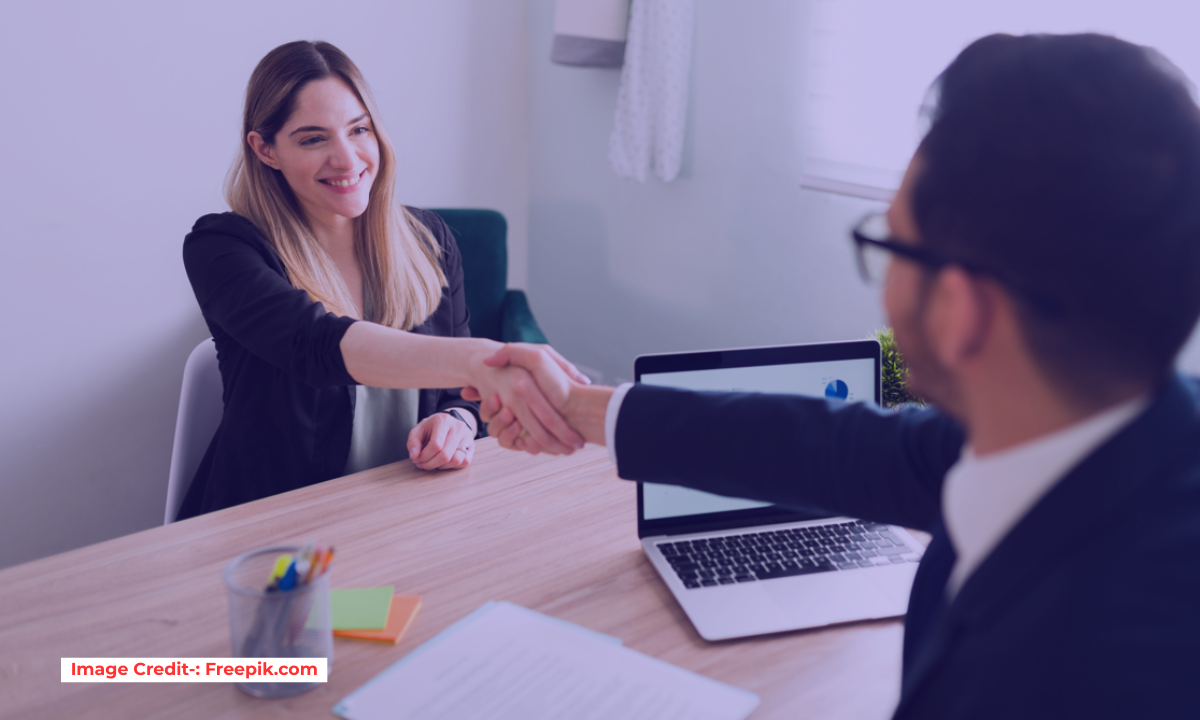
Here are the top interview questions for mechanical engineers, selected for how frequently they appear and how well they test both your technical knowledge and problem-solving abilities.
The table below organizes these questions by category to help you structure your preparation.
| Category | Question | What Interviewers Look For |
|---|---|---|
| Core Technical | Explain the Second Law of Thermodynamics. | Understanding of fundamental energy concepts and real-world application. |
| Core Technical | Differentiate between heat and temperature. | Conceptual clarity on basic but crucial principles. |
| Core Technical | What is the purpose of a flywheel? | Knowledge of machine elements that manage energy and motion. |
| Core Technical | What is the difference between tensile stress and compressive stress? | Understanding of material science and structural behavior under load. |
| Design & Software | What CAD software are you proficient in, and how have you used it on a project? | Practical, hands-on skill with essential design tools and ability to apply them. |
| Design & Software | What is GD&T and why is it important? | Knowledge of manufacturing standards and precision in design. |
| Behavioral | Describe a project where you faced a significant engineering challenge. How did you overcome it? | Problem-solving skills, resilience, and structured approach to obstacles (often assessed with STAR method). |
| Behavioral | Tell me about a time you had to work under a tight deadline. | Time management, performance under pressure, and planning abilities. |
| Behavioral | Describe your experience working in a team setting. | Collaboration, communication skills, and ability to contribute in a group. |
| General | Tell me about yourself. | Concise professional summary, background, and career goals alignment. |
💡 How to Structure Your Answers-:
Beyond knowing the questions, how you answer them is critical. Here are proven strategies for crafting your responses.
-
Use the STAR Method for Behavioral Questions: This technique ensures your answers are structured and impactful.
-
Situation: Briefly describe the context.
-
Task: What was your specific goal or responsibility?
-
Action: What specific steps did you take? Use “I” to focus on your actions.
-
Result: What was the outcome? Quantify your success with numbers when possible (e.g., “increased efficiency by 15%”).
-
-
Combine Theory and Practice for Technical Questions: Don’t just state a definition. Follow up with a real-world application or example to show you truly understand the concept. For instance, after defining the second law of thermodynamics, you could explain its implications for engine efficiency.
-
Tailor Your CAD Experience: When discussing CAD software, don’t just list programs. Describe a specific project where you used them, your role, the tools/features you applied, and the impact of your work.
🛠️ Preparation Beyond the Questions-:
Thorough preparation involves more than memorizing answers.
-
Review Core Subjects: Focus on key areas like Strength of Materials, Thermodynamics, Fluid Mechanics, and Manufacturing Processes. Be prepared to apply these concepts to practical problems.
-
Prepare Your Own Questions: Interviews are a two-way street. Prepare thoughtful questions about the company’s projects, team culture, or technologies they use. This shows genuine interest and engagement.
-
Practice Aloud: Rehearse your answers out loud to build fluency and confidence. This helps you sound more polished and natural during the actual interview.
🎯 Level-Specific Focus-:
-
For Freshers: Emphasize your academic projects, internships, and enthusiasm to learn. Your CAD skills and ability to apply theoretical knowledge will be closely examined.
-
For Experienced Engineers: You will be expected to provide detailed examples from your past work, demonstrating leadership, project management, and deep technical expertise in your field.