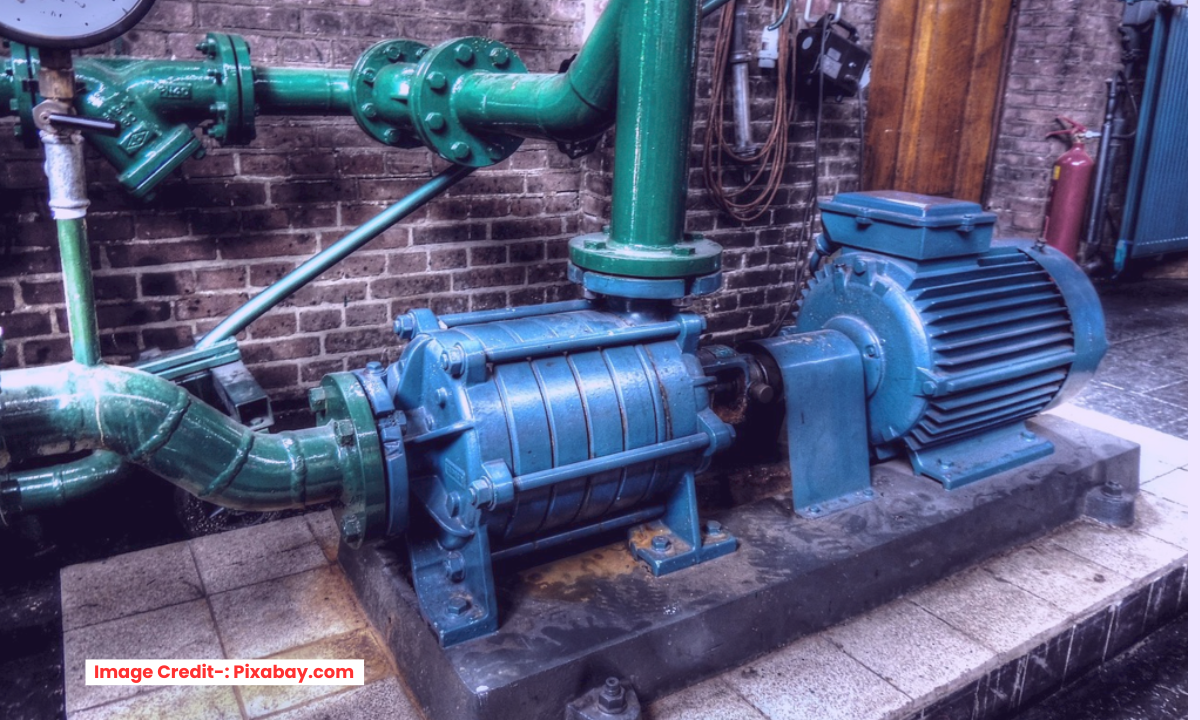
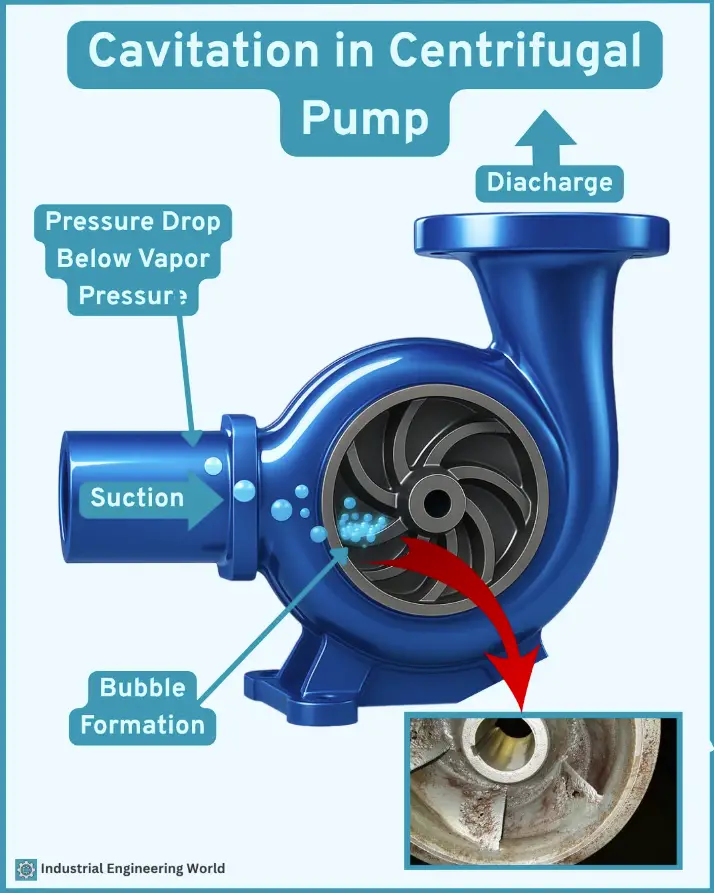
Cavitation is a destructive phenomenon that occurs in centrifugal pumps when the liquid pressure drops below its vapor pressure, causing the formation and collapse of vapor bubbles. This leads to noise, vibration, and severe damage to pump components.
1. What Causes Cavitation in Centrifugal Pumps?
Cavitation in centrifugal pumps is fundamentally caused by the formation and subsequent collapse of vapor bubbles within the liquid. Primary Causes are as follows:
-
Low Inlet Pressure (NPSH-A < NPSH-R)
-
Net Positive Suction Head Available (NPSH-A) is too low compared to NPSH Required (NPSH-R) by the pump.
-
Common in high-speed pumps or systems with long suction lines.
-
-
High Fluid Temperature
-
Hot liquids have higher vapor pressure, increasing cavitation risk.
-
-
Clogged Strainers/Filters
-
Restricts flow, reducing suction pressure.
-
-
Improper Pump Sizing
-
Oversized pumps running at low flow rates can cause recirculation and cavitation.
-
-
Excessive Pump Speed
-
Higher RPMs increase suction pressure drop.
-
Related posts:
- Top 10 Courses to Join After Mechanical Engineering
- BRL-CAD: Open-Source Software for Military Engineering
- 3DViewStation Bridges Gap Between Engineers and Suppliers
2. Effects of Cavitation-:
| Symptom | Impact |
|---|---|
| Loud Noise | Sounds like gravel or marbles rattling inside the pump. |
| Vibration | Premature bearing and seal failure. |
| Pitting/Erosion | Bubble collapse damages impeller, casing, and vanes. |
| Reduced Efficiency | Loss of flow rate & pressure due to vapor blockage. |
| Seal & Bearing Damage | Cavitation-induced vibrations reduce component lifespan. |
3. How to Prevent Cavitation-:
A. Increase NPSH-A (Available Suction Pressure)-:
✔ Raise Liquid Level (e.g., elevate supply tank).
✔ Use Larger Suction Pipes (reduce friction losses).
✔ Reduce Pipe Fittings (minimize bends/valves).
B. Reduce NPSH-R (Pump’s Required Suction Pressure)-:
✔ Use a Low-NPSH-R Impeller (e.g., inducer-type).
✔ Lower Pump Speed (if possible).
C. System Design Adjustments-:
✔ Avoid Air Leaks (check suction line connections).
✔ Install a Booster Pump (for low-pressure systems).
✔ Cool the Liquid (if high temperature is the issue).
D. Operational Best Practices-:
✔ Avoid Running at Low Flow (prevent recirculation).
✔ Monitor Pump Performance (use vibration sensors).
4. How to Detect Cavitation Early-:
-
Noise & Vibration Analysis (ultrasonic sensors help detect bubble collapse).
-
Performance Drop (monitor flow, pressure, and efficiency).
-
Visual Inspection (check impeller for pitting).
Conclusion
Cavitation is a serious issue that can destroy a centrifugal pump if left unchecked. Prevention is key—ensure proper NPSH margin, optimize system design, and monitor pump health.
Related Posts:
- Ultimate Guide to Landing Your First Mechanical Engineering Job
- From Mechanical Design Engineer to Engineering Manager: Making the Leap
- How to Negotiate Your Engineering Salary Like a Pro
“Thank you for reading! If you found this article insightful and valuable, consider sharing it with your friends and followers on social media. Your share can help others discover this content too. Let’s spread knowledge together. Your support is greatly appreciated!”