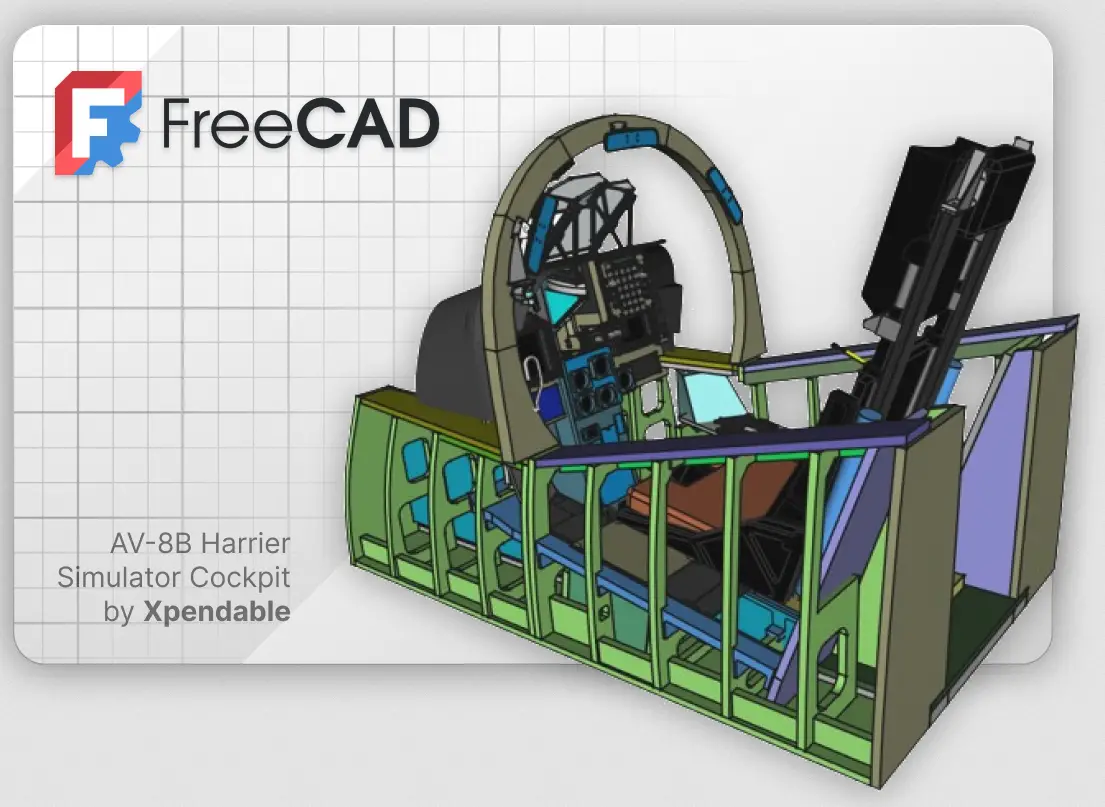
FreeCAD is an open-source parametric 3D design software that offers a no-cost introduction to the world of 3D modeling. As a powerful and versatile tool, FreeCAD allows users to create precise and detailed models for a wide range of applications, including engineering, architecture, and product design. With its intuitive interface and extensive set of features, getting started with FreeCAD is straightforward for both beginners and experienced designers alike.
Users can leverage its parametric modeling capabilities to easily make changes to their designs at any point in the process, ensuring flexibility and ease of editing. Additionally, FreeCAD supports a variety of file formats, making it compatible with other popular CAD software. Whether you are looking to create simple objects or intricate designs, FreeCAD provides a solid foundation for exploring the world of 3D design without any financial barriers.
Related Posts-:
| How to Clone and Rotate Body in FreeCAD |
| Get Mass Properties, Weight, Volume and Area etc. in FreeCAD |
| How to use Texture Mapping in FreeCAD |
Absolutely! FreeCAD is an excellent zero-cost solution for anyone looking to dive into 3D design, whether you’re a hobbyist, student, educator, or professional. Here’s why FreeCAD stands out as a free and powerful tool for 3D design, along with tips to get started:
Why Choose FreeCAD?
FreeCAD is a versatile, open-source parametric 3D modeling software that is an excellent choice for professionals in various industries such as architecture, engineering, and product design. Its ability to create complex designs with precision and accuracy make it a valuable tool for professionals looking to streamline their workflow. FreeCAD’s parametric modeling feature allows users to easily go back and make changes to their designs without having to start from scratch, saving time and increasing efficiency. Additionally, FreeCAD supports a wide range of file formats making it compatible with other software tools commonly used in professional settings. With its robust features, user-friendly interface, and active community support, choosing FreeCAD can provide professionals with the tools they need to create high-quality designs effectively and efficiently.
- Completely Free and Open-Source:
- FreeCAD is licensed under the LGPL-2.0 license, meaning it’s free to download, use, modify, and distribute.
- No subscription fees or hidden costs, unlike many commercial CAD tools.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- FreeCAD runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it accessible to users on any operating system.
- Parametric Modeling:
- FreeCAD uses a parametric approach, allowing you to easily modify your designs by changing parameters and constraints.
- Versatile Workbenches:
- FreeCAD offers specialized workbenches for different tasks, such as:
- Part Design: For creating 3D parts.
- Sketcher: For 2D sketching and constraints.
- Architecture (Arch): For building design and BIM.
- FEM: For finite element analysis.
- Path: For CNC machining and toolpath generation.
- TechDraw: For creating 2D technical drawings.
- FreeCAD offers specialized workbenches for different tasks, such as:
- Extensible and Customizable:
- FreeCAD supports Python scripting, allowing you to automate tasks or create custom tools.
- A growing library of add-ons and macros extends its functionality.
- Active Community:
- FreeCAD has a vibrant and supportive community of users and developers.
- Forums, tutorials, and documentation are readily available to help you learn and troubleshoot.
Related Posts-:
- Model Involute Gear in FreeCAD
- Let’s understand FreeCAD Part Workbench
- Let’s Explore the FreeCAD user Interface
Getting Started with FreeCAD-:

FreeCAD is an open-source parametric 3D modeling software that offers professional users a powerful tool for designing and creating detailed models. Getting started with FreeCAD involves familiarizing oneself with its intuitive user interface, which includes features such as sketching, part design, and assembly tools. To begin a project, users can create sketches of their desired shapes and then use various tools to extrude, revolve, or loft these sketches into 3D objects.
Additionally, FreeCAD supports the creation of complex assemblies by allowing users to define constraints between different parts. By mastering the basic functionalities of FreeCAD, professionals can leverage its advanced capabilities such as creating designs for mechanical engineering projects, architectural drawings, or even 3D printing models. Overall, learning how to navigate and utilize FreeCAD effectively is essential for any professional looking to enhance their design workflow and produce high-quality CAD models.
- Download and Install:
- Visit the official FreeCAD website: https://www.freecad.org.
- Download the version compatible with your operating system.
- Follow the installation instructions.
- Explore the Interface:
- Familiarize yourself with the interface, including the 3D view, tree view, property editor, and workbench selector.
- Take a tour of the different workbenches to understand their purposes.
- Learn the Basics:
- Start with the Sketcher workbench to create 2D sketches.
- Use the Part Design workbench to turn sketches into 3D models.
- Experiment with constraints and parameters to understand parametric modeling.
- Follow Tutorials:
- FreeCAD’s official documentation includes beginner-friendly tutorials: FreeCAD Documentation.
- Check out YouTube channels like Joko Engineeringhelp, MangoJelly Solutions, and FreeCAD Academy for video tutorials.
- Join the Community:
- Participate in the FreeCAD Forum: https://forum.freecad.org.
- Ask questions, share your projects, and learn from others.
- Experiment and Practice:
- Start with simple projects, such as designing a basic mechanical part or a small household item.
- Gradually move on to more complex designs as you gain confidence.
Related Posts-:
- Setup Auto Spacing in FreeCAD Sketcher
- Easily Slice Part with Plane in FreeCAD
- Insert Surface Finish Symbol in FreeCAD Drawing
FreeCAD Use Cases-:
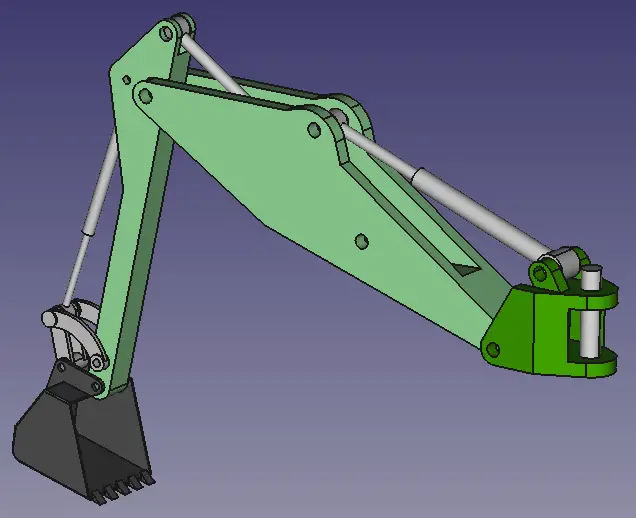
FreeCAD is a versatile and powerful open-source 3D modeling software that is widely used across various industries. One of the top use cases of FreeCAD is in mechanical engineering, where it can be utilized for creating detailed 3D models of machine parts, prototypes, and assemblies. Another common use case is in architecture and civil engineering, where FreeCAD can help architects and designers visualize building structures and plan construction projects. Additionally, FreeCAD is commonly used in the field of product design to develop innovative product concepts and prototypes. Furthermore, FreeCAD can also be applied in the realm of robotics for designing complex robot components and assemblies. Overall, FreeCAD’s intuitive interface, extensive library of tools, and flexible design capabilities make it a valuable tool for professionals in various industries seeking reliable 3D modeling software for their projects.
- Hobbyists: Create 3D models for 3D printing, robotics, or DIY projects.
- Students: Learn 3D design and engineering concepts without spending money on software.
- Educators: Teach CAD, architecture, or engineering using a free and accessible tool.
- Professionals: Use FreeCAD for prototyping, product design, or small-scale manufacturing.
Related Posts-:
- Measure Area, Volume & Center of Mass with Python Script
- Import Existing FreeCAD Setting on Fresh FreeCAD Installation
- FreeCAD with Python Scripting. Make Tools and Workflows
Tips for FreeCAD Success-:

To achieve success in using FreeCAD, it is imperative to familiarize oneself with the software’s interface and functionalities. Begin by exploring the various workbenches available and understanding their respective tools and features. Additionally, stay updated with tutorials, forums, and online resources to continuously enhance your skills and knowledge of FreeCAD. Pay attention to precision while drafting designs, as accuracy is crucial in creating professional-grade models. Utilize constraints, measurements, and reference geometries effectively to ensure accurate dimensions and alignments within your designs. Furthermore, always save your work regularly to prevent data loss and consider utilizing version control systems for larger projects. Lastly, do not hesitate to seek help from the FreeCAD community when facing challenges or seeking advice on how to optimize your workflow for maximum efficiency. By following these tips diligently, you can elevate your proficiency in FreeCAD and attain successful outcomes in your design projects.
- Be Patient: FreeCAD has a learning curve, especially if you’re new to CAD. Take your time to understand the tools and workflows.
- Use Constraints Wisely: Constraints in the Sketcher workbench are powerful but can be tricky. Practice using them effectively.
- Leverage Add-ons: Explore the FreeCAD Addon Manager to install useful extensions like Fasteners, Assembly4, or Render workbenches.
- Backup Your Work: Save your projects frequently to avoid losing progress.
Related Posts-:
- How to Clone and Rotate Body in FreeCAD
- Free Online Tool to View CAD Files
- Easily Rotate Sketch in FreeCAD
Conclusion
FreeCAD is a fantastic zero-cost way to start your journey into 3D design. Its open-source nature, combined with its powerful features and active community, makes it a compelling choice for anyone interested in CAD. Whether you’re designing for 3D printing, engineering, or architecture, FreeCAD provides the tools you need to bring your ideas to life—without breaking the bank.
“Thank you for reading! If you found this article insightful and valuable, consider sharing it with your friends and followers on social media. Your share can help others discover this content too. Let’s spread knowledge together. Your support is greatly appreciated!”