Hello friends welcome to SolidWorks Tutorial In this tutorial we will Understand How to Speed Up SolidWorks Performance. If you want to learn SolidWorks from scratch then you can buy my Complete SolidWorks Course : From Zero to Expert! on Udemy. The slow performance of SolidWorks can be caused by multiple factors, ranging from hardware limitations to software settings and inefficient modeling practices. with every new release of SolidWorks it release note and minimum hardware requirement so check the release note weather you have minimum hardware to run SolidWorks. Here are some tips and tricks to speed up SolidWorks performance and improve your workflow:
Related Posts-:
- Understand Reference Triad in SolidWorks
- Understand Accepting Features in SolidWorks
- Create Forming Tool in SolidWorks for Sheet Metal Part
Tips to Speed Up SolidWorks Performance-:
1. Optimize Your Hardware-:
Optimizing hardware for SolidWorks involves selecting components that maximize performance for CAD modeling, simulations (FEA/CFD), and rendering. When SolidWorks release new version it also release minimum hardware requirement to that version.
Optimizing your hardware to boost SolidWorks performance involves focusing on key components that the SolidWorks Software relies on. SolidWorks is primarily CPU-bound for most tasks (e.g., modeling, drafting, detailing & simulations), but GPU acceleration helps in rendering and real-time graphics.
- RAM: Ensure your computer has sufficient RAM (16 GB minimum, 32 GB or more recommended for large assemblies). For small assemblies in SolidWorks minimum 16 GB of RAM is must and recommended RAM for medium-large assemblies & simulations is in range from 32GB–64GB.
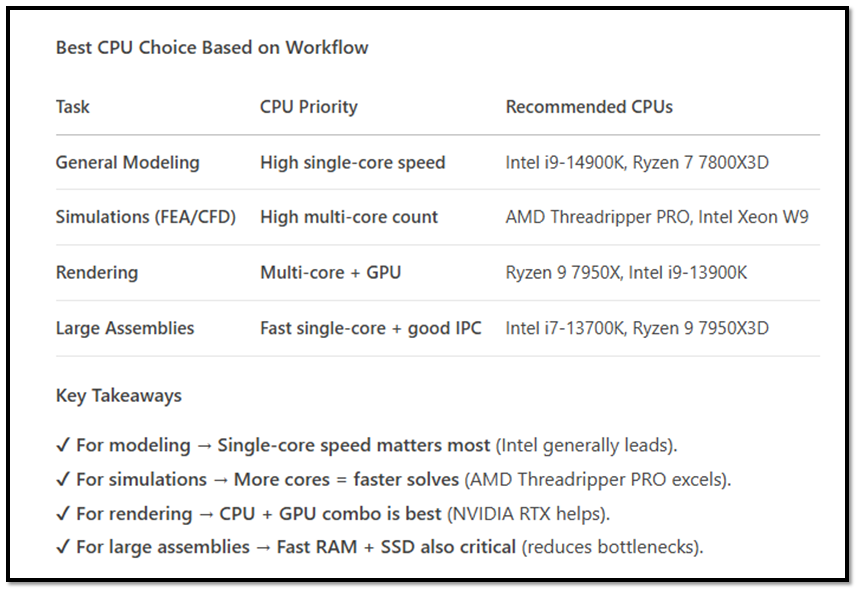
- CPU: SolidWorks is a smart CAD tool hence utilizes CPU cores differently depending on the task weather you are doing modeling & performing FEA . A faster multi-core processor can significantly improve performance. For boosting SolidWorks performance, the CPU is the most critical component because SolidWorks relies heavily on single-core speed for most modeling operations. (part/assembly editing, sketches, feature rebuilding). However, simulations (FEA/CFD) and rendering can leverage multiple cores.
- GPU: While SolidWorks is primarily CPU-dependent for modeling and calculations, a good GPU significantly enhances real-time graphics, rendering, and display performance. Use a certified graphics card with updated drivers. Check SolidWorks’ certified hardware list. A good GPU Provides realistic shading, shadows, and reflections in real-time. it helps to Smooth manipulation of complex models. lets understand GPU importance with an example Rotating a large assembly is much smoother with an NVIDIA RTX A5000 vs. integrated graphics. A powerful GPU reduces lag when zooming/panning in assemblies with 10,000+ parts. A good GPU helps to Generates photorealistic images & animations.
- SSD: SolidWorks relies heavily on storage speed for loading files, saving changes, and managing large assemblies. Upgrading to a fast SSD (NVMe PCIe 4.0/5.0) can significantly improve performance. NVMe SSDs (3,000-7,000 MB/s) reduce load times by 5-10x. Example: A 500MB assembly loads in 2-3 sec (NVMe SSD) vs. 15-30 sec (HDD). SolidWorks have inbuilt feature known as Auto save to prevent work loss if you are using HDDs then it will cause lag spikes on the other hand if you are using SSD then No stuttering during background saves. While performing FEA/CFD simulation in SolidWorks that generate temporary cache files if you are using SSD aster read/write speeds reduce solve times.
Related Posts-:
- Create Keyboard Shortcut in SolidWorks
- How to use Sweep Features in SolidWorks
- How to Use the Loft Feature in SolidWorks
2. Adjust System Settings-:
a. SolidWorks Settings
- OpenGL Mode: Enable OpenGL software mode for better performance on some systems (
Tools > Options > Performance > Use Software OpenGL). - Level of Detail: Adjust the level of detail for large assemblies (
Tools > Options > Display > Assembly Transparency for In Context Edit). - Rebuild on Save: Disable rebuild on save to speed up saving (
Tools > Options > System Options > Performance > Rebuild on Save).
b. Windows Settings
- Power Plan: Set your power plan to
High Performancein Windows Control Panel. - Visual Effects: Adjust for best performance (
Control Panel > System > Advanced system settings > Performance Settings > Adjust for best performance).
3. Simplify Your Model
- Break Down Complex Models: Divide large assemblies into smaller sub-assemblies.
- Use Simplified Configurations: Create simplified configurations with fewer details for faster performance.
- Suppress Features: Suppress features that are not currently needed (
Right-click on feature > Suppress).
4. Optimize Assemblies
- Lightweight Components: Open components in lightweight mode (
Tools > Options > System Options > Performance > Automatically load components lightweight). - Large Assembly Mode: Enable large assembly mode for better performance with large assemblies (
Tools > Large Assembly Mode). - Use SpeedPak: Create SpeedPak configurations to reduce the load on your system (
Right-click on assembly > SpeedPak > Create SpeedPak).
5. Manage Your Feature Tree
- Hide Unnecessary Features: Hide features that are not currently being worked on.
- Use Folders: Organize features into folders to keep the feature tree manageable.
- Freeze Bar: Use the freeze bar to suppress features below it (
Drag the freeze bar in the feature tree).
6. Optimize Drawings
- High-Quality Views: Use draft quality for views that do not require high detail (
Right-click on view > Properties > Display Style > Draft Quality). - Hide Components: Hide components that are not needed in the drawing.
- Use Detached Drawings: Open drawings in detached mode for faster performance (
File > Open > Detached Drawings).
7. Use Efficient Workflows
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Learn and use keyboard shortcuts to speed up your workflow.
- Macros: Use macros to automate repetitive tasks.
- Design Library: Use the design library to quickly insert standard parts and features.
8. Update SolidWorks
- Install the Latest Version: Always use the latest version of SolidWorks to benefit from performance improvements and bug fixes.
- Check for Updates: Regularly check for updates and install them.
9. Example: Optimizing a Large Assembly
Here’s an example of optimizing a large assembly:
- Break Down the Assembly: Divide the assembly into smaller sub-assemblies.
- Use Simplified Configurations: Create simplified configurations with fewer details.
- Suppress Features: Suppress features that are not currently needed.
- Open Components in Lightweight Mode: Enable lightweight mode for components.
- Use SpeedPak: Create SpeedPak configurations to reduce the load on your system.
- Hide Unnecessary Components: Hide components that are not needed in the current view.
10. Conclusion
By following these tips and tricks, you can significantly speed up SolidWorks performance and improve your workflow. Optimize your hardware, adjust system settings, simplify your models, and use efficient workflows to get the most out of SolidWorks. Happy designing!
“Thank you for reading! If you found this article insightful and valuable, consider sharing it with your friends and followers on social media. Your share can help others discover this content too. Let’s spread knowledge together. Your support is greatly appreciated!”