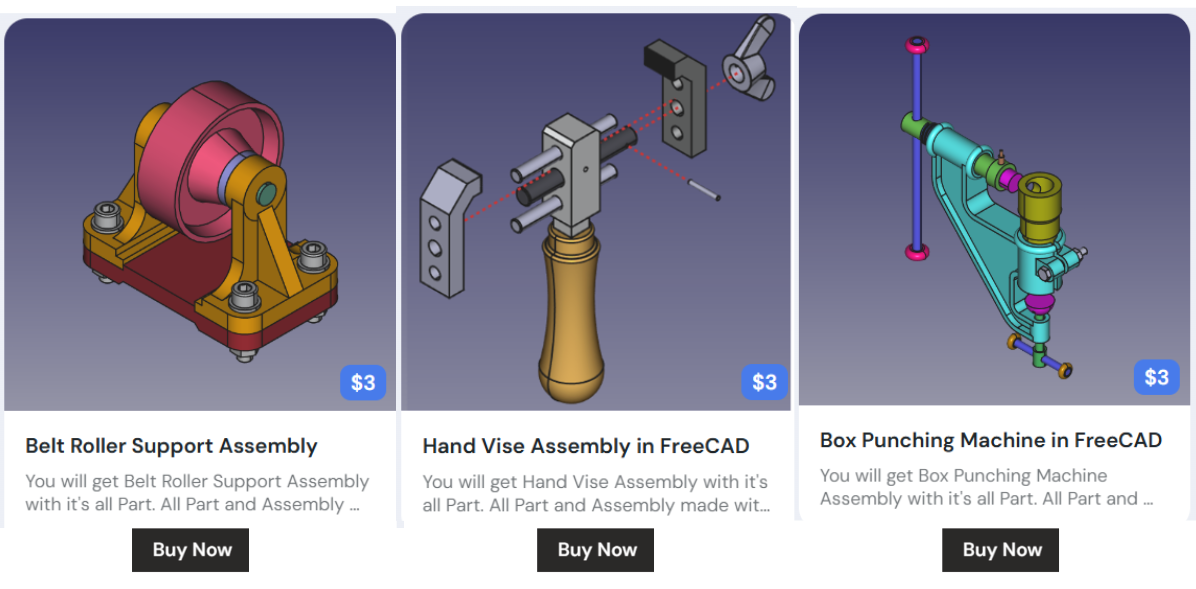
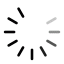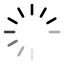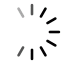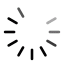
For small organization where operation cost reduction and maximizing profit is a big challenge. FreeCAD can play a big role to help small organization to reduce their operating cost because it is Free and open-source. In recent years FreeCAD emerge as No-Cost Solution for 3D Design for Hobbyist and Freelancer who want to start their CAD services.
FreeCAD is an excellent zero-cost solution for anyone looking to start 3D design. Whether you’re a student, hobbyist, or professional, FreeCAD offers a wide range of tools and features to help you create detailed 3D models. Here’s a guide to getting started with FreeCAD for 3D design. FreeCAD is a powerful open-source parametric 3D design software that offers a no-cost solution for users looking to create detailed and intricate designs. With its user-friendly interface and comprehensive set of tools, FreeCAD allows for the creation of complex structures, models, and prototypes with ease.
Related Posts-:
To get started with FreeCAD, users can download the software from the official website or GitHub repository. The program supports various file formats including STEP, IGES, STL, SVG, and DXF, making it compatible with other CAD programs. Users can utilize features such as sketching, constraints, assemblies, and rendering to bring their designs to life. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced designer looking for a cost-effective solution for 3D modeling, FreeCAD provides the necessary tools and capabilities to bring your ideas into reality.
1. Why Choose FreeCAD ?

FreeCAD is an excellent choice for professionals in various industries due to its robust features and capabilities. This open-source parametric 3D modeling software offers a wide range of tools for designing complex mechanical, architectural, and electrical models with precision and accuracy. FreeCAD supports a variety of file formats, making it compatible with other CAD software commonly used in professional settings. Furthermore, FreeCAD’s intuitive interface and customizable design workflow allow users to streamline their design process and increase productivity.
Additionally, the active online community provides extensive support and resources for troubleshooting any issues that may arise during the design process. Overall, professionals can trust FreeCAD to deliver high-quality designs efficiently and effectively for their projects.
- Free and Open-Source: No cost, making it accessible for everyone.
- Cross-Platform: Works on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Parametric Modeling: Create flexible designs that can be easily modified.
- Extensible: Customize and extend functionality with Python scripting.
- Active Community: Access to forums, tutorials, and user-contributed resources.
Related Posts-:
- Advantages of FreeCAD That Every FreeCAD user Must Know
- Power of FreeCAD: Essential Tools for Mechanical Engineers
- Enhance Design Skills: Essential FreeCAD Tips for Better Creations
2. Getting Started with FreeCAD-:
Getting started with FreeCAD is a comprehensive and versatile approach to computer-aided design (CAD) software. This powerful open-source program offers a wide range of features, including parametric modeling, robot simulation, and architecture design tools. To begin using FreeCAD effectively, it is important to familiarize yourself with the user interface and the various workbenches available for different types of projects. The Part Design workbench is ideal for creating 3D models, while the Sketcher workbench allows for precise 2D sketches that can be extruded into 3D shapes.
Additionally, mastering the Draft workbench enables users to create 2D drawings and architectural blueprints. With its intuitive tools and active community support, FreeCAD is an excellent choice for professionals looking to explore CAD software without the burden of licensing fees.
a. Download and Install FreeCAD-:
At the time of writing the post FreeCAD current stable version is 1.0 which is available for major operating system Windows, Man and Linux. FreeCAD’s development happens daily! The FreeCAD community generates weekly builds that are based on bleeding edge FreeCAD code in order for users to test bugfixes/regressions along with new features. We ask that advanced users occasionally run the development builds to assist with testing new code. These builds are not suitable for production use, and care should be taken when using them (back up your files regularly, etc.). Development builds should be expected to be slower, consume more memory, and be less stable than the official release versions.
Download here a Weekly Build for Windows, macOS or Linux. On Linux, Snap and Flatpak also provide development channels.
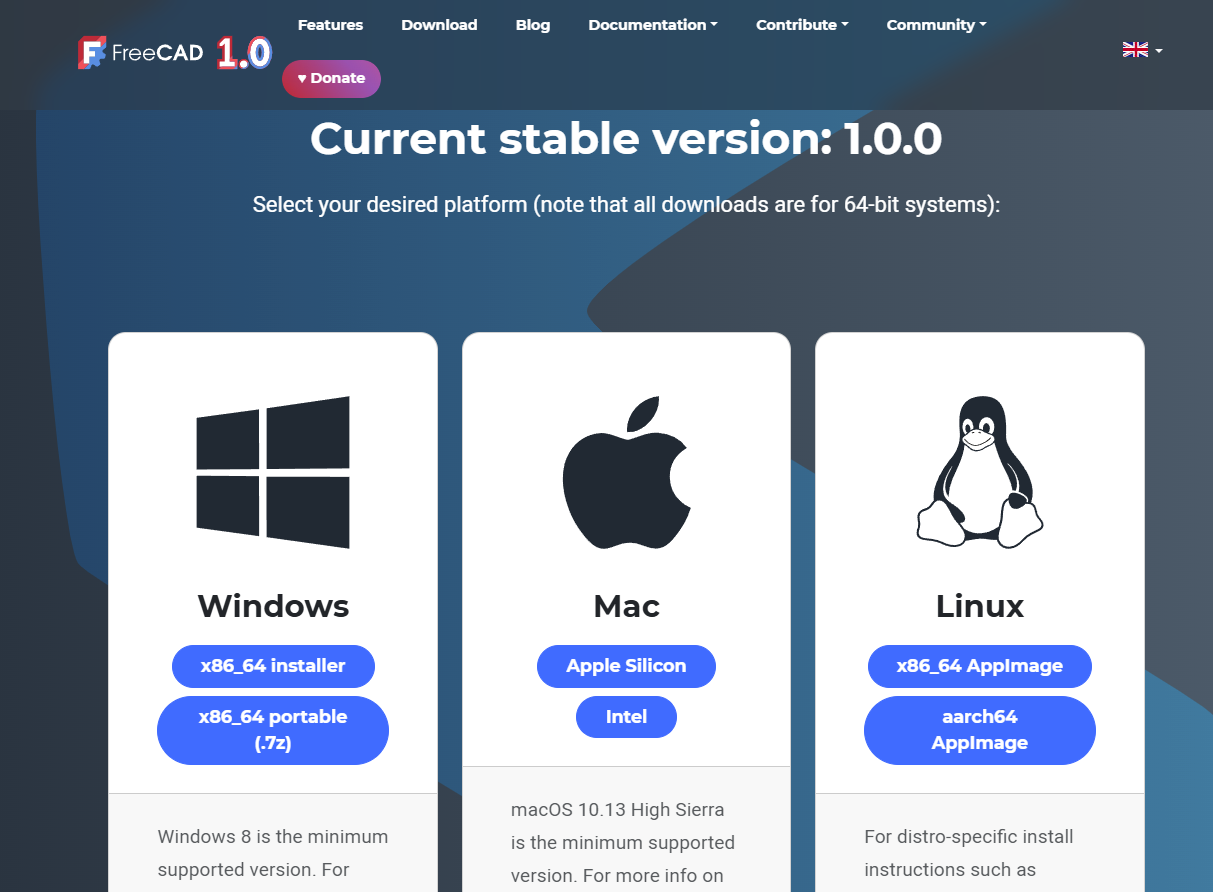
- Visit the FreeCAD website and download the latest version for your operating system.
- Follow the installation instructions with respect to your operating system.
Also Read-:
| Easily Rotate Sketch in FreeCAD |
| Create Keyboard Short cut in FreeCAD |
| Easily Slice Part with Plane in FreeCAD |
b. Explore the FreeCAD Interface-:
The FreeCAD interface is based on Qt, a well known graphical user interface (GUI) toolkit, particularly used in Linux, but also available in Windows and MacOS.
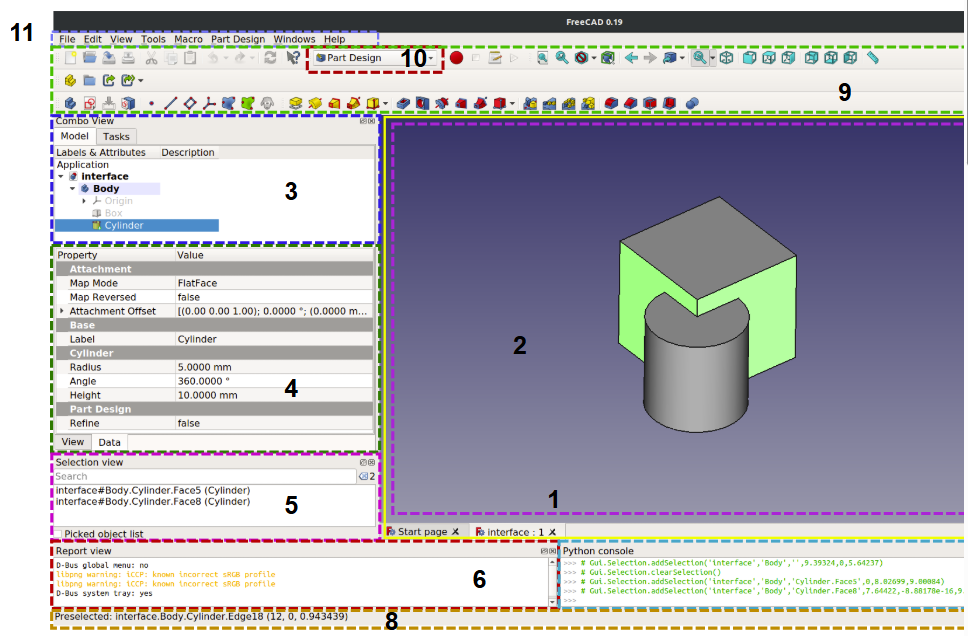
- The main window of the application can be roughly divided into 11 sections:
- The main view area, which can contain different tabbed windows
- The 3D view, normally embedded in the main view area
- The upper part of the combo view, which includes the tree view and task panel
- The lower part of the combo view, which includes the property editor
- The selection view
- The report view
- The Python console
- The status bar
- The toolbar area, see the following information on the toolbars
- The Workbench selector, which itself is a toolbar
- The standard menu
- Familiarize yourself with the interface, including:
- Workbenches: Specialized tool sets for different tasks (e.g., Part Design, Sketcher, Arch).
- Model Tree: Displays the structure of your design.
- Properties Editor: Allows you to modify object properties.
- Python Console: For scripting and automation.
Related Posts-:
- FreeCAD vs. Fusion 360: Which one is Best CAD Software
- Exploring FreeCAD Macros and Python Scripting
- FreeCAD Community: Connect and Collaborate with Users
3. Key Workbenches for 3D Design-:
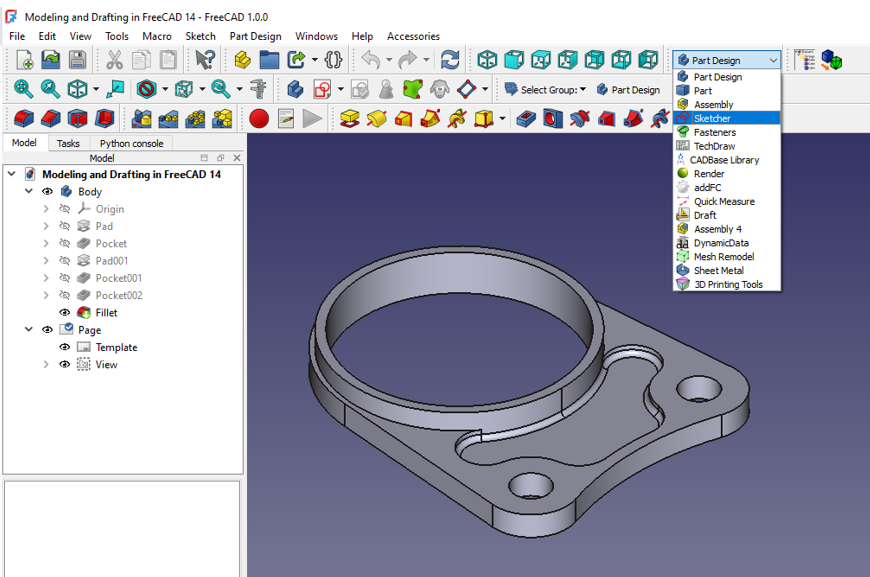
In FreeCAD, a popular open-source parametric 3D modeling software, key workbenches play a crucial role in streamlining the design process. The Part Design workbench is essential for creating complex 3D models by allowing users to sketch 2D shapes and convert them into solid objects through extrusion or revolve operations. The Sketcher workbench provides the foundation for creating these sketches with tools for precise dimensioning and constraints, ensuring accuracy and flexibility in designs.
Additionally, the Draft workbench enables users to manipulate 2D shapes in three dimensions, facilitating tasks such as copying, scaling, and rotating objects within a design. These key workbenches combine to provide a comprehensive set of tools for 3D design in FreeCAD, empowering users to bring their creative visions to life with efficiency and precision.
a. FreeCAD Sketcher Workbench-:
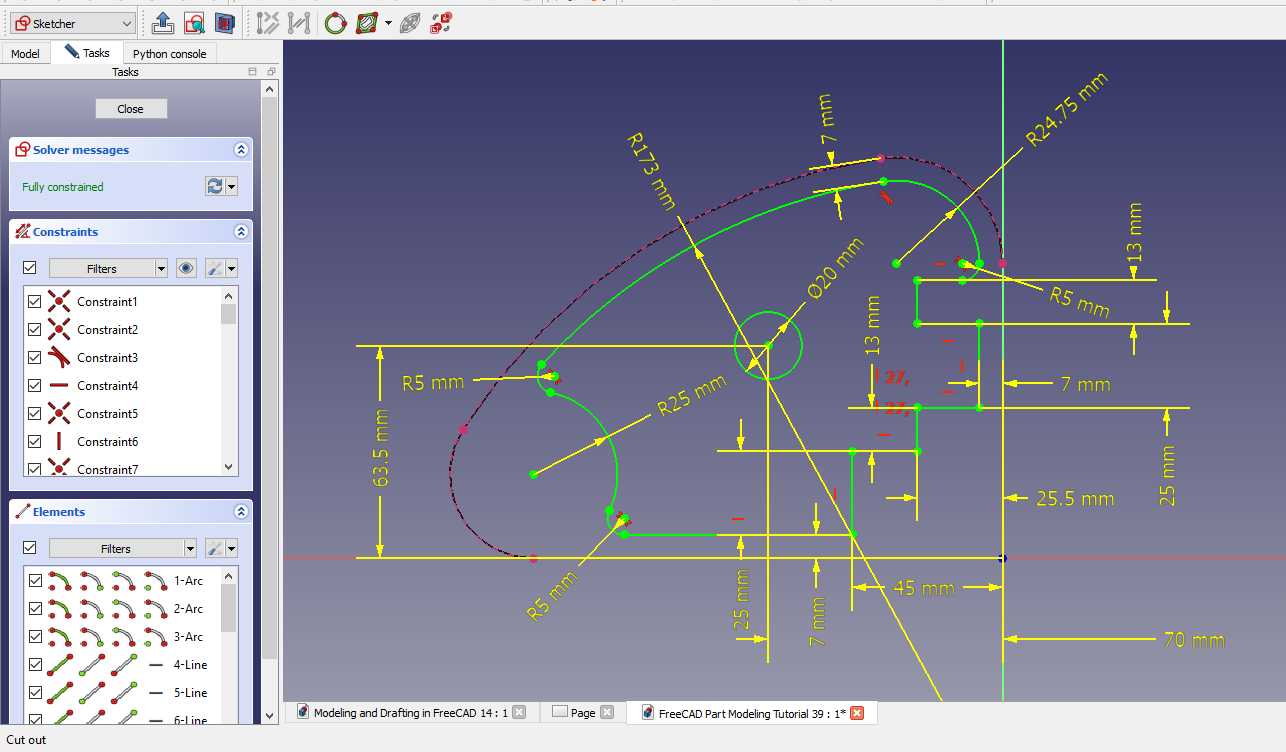
The FreeCAD Sketcher Workbench is a powerful and versatile tool that allows professionals to create complex 2D sketches with precision and ease. With features such as constraint-based sketching, users can easily define relationships between different elements within their sketches, ensuring accuracy and consistency throughout the design process.
The Sketcher Workbench also offers a wide range of tools for adding dimensions, constraints, and geometric shapes to sketches, making it ideal for engineers, architects, and designers working on intricate projects. Additionally, the ability to easily convert these 2D sketches into 3D models within FreeCAD further enhances its utility in professional settings. Overall, the Sketcher Workbench in FreeCAD is a valuable resource for professionals seeking to streamline their design workflow and produce high-quality models with efficiency and precision.
- Purpose: Create 2D sketches.
- Key Tools: Lines, circles, rectangles, constraints.
Related Posts-:
- Unlock the Power of FreeCAD: How to Start Using Macros Today
- FreeCAD Community: A Guide to Connecting and Collaborating with Users
- How FreeCAD Becomes a Student’s Best Friend in Learning CAD
b. FreeCAD Part Design Workbench-:
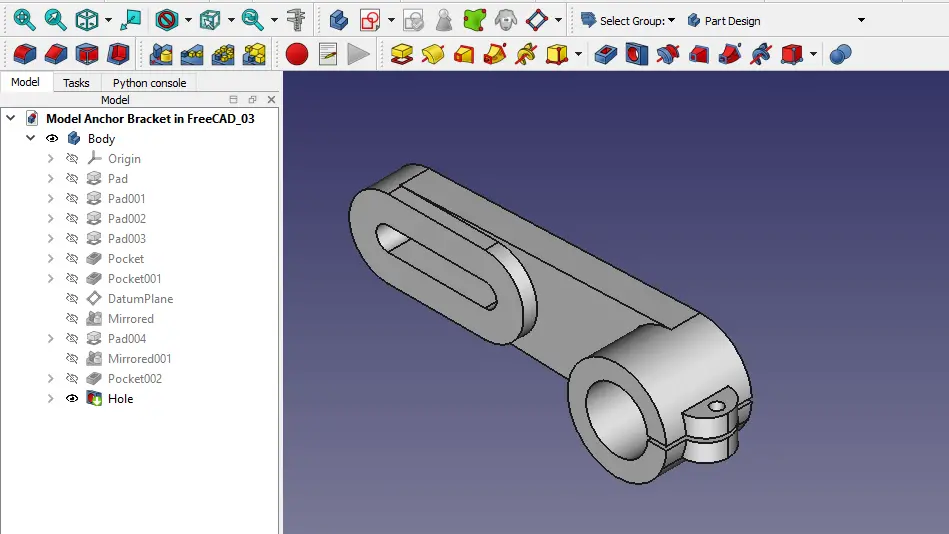
The FreeCAD Part Design Workbench is a powerful 3D modeling tool designed for professional engineers and designers. This dedicated workbench allows users to create complex 3D models with precision and ease, enabling them to design intricate parts and components with accuracy. With a comprehensive set of tools and features such as sketching, constraints, fillets, chamfers, and boolean operations, the Part Design Workbench gives users the flexibility to create detailed and realistic models that meet industry standards. In addition, its parametric capabilities allow for easy modifications and iterations throughout the design process, ensuring efficient workflow and optimal results. Overall, the FreeCAD Part Design Workbench is an essential tool for professionals in various industries seeking advanced 3D modeling capabilities for their projects.
- Purpose: Create 3D models from sketches.
- Key Tools: Pad, Pocket, Revolution, Loft.
c. FreeCAD Part Workbench-:
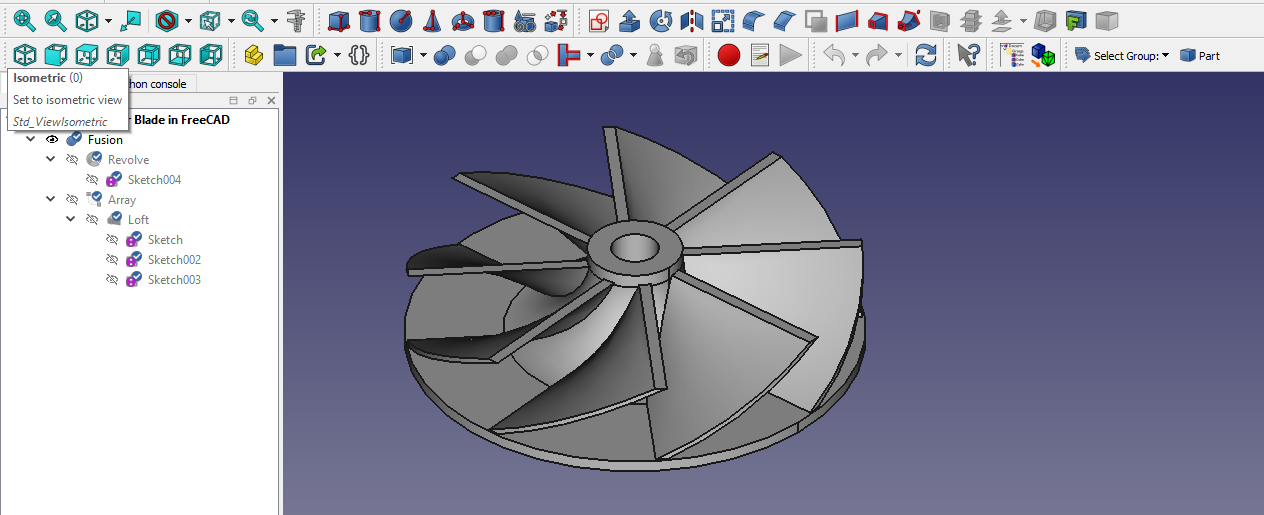
The Part Workbench provides a traditional constructive solid geometry (CSG) workflow. In this workflow each object is an independent solid. The Part Workbench can create them from parametrically defined sketches using tools like Extrude, Revolve, Loft, etc. In addition, basic primitive solids like Cube, Cylinder, etc. can be created as well. These objects can be combined, through Boolean operations, to create more complex solids.
The Part Workbench can also create objects that are not solids, such as faces, shells, and objects with only edges or vertices. It also provides a variety of general purpose tools for geometry manipulation, geometry validation, and making copies.
The FreeCAD Part Workbench is a powerful and versatile tool used for creating, modifying, and analyzing 3D solid models. As part of the open-source FreeCAD software suite, the Part Workbench allows users to design complex mechanical components with precision and ease. With a wide range of features including sketching tools, Boolean operations, and parametric modelling capabilities, this workbench enables engineers and designers to efficiently develop parts for various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and product design.
Additionally, its seamless integration with other workbenches within FreeCAD offers a comprehensive design environment for professionals looking to create detailed and accurate 3D models. Whether creating simple geometries or intricate assemblies, the FreeCAD Part Workbench provides a flexible solution for professionals seeking advanced CAD functionality.
- Purpose: Create and modify basic geometric shapes.
- Key Tools: Box, Cylinder, Sphere, Boolean operations.
d. Draft Workbench
- Purpose: Create 2D drawings and annotations.
- Key Tools: Lines, arcs, dimensions.
e. TechDraw Workbench
- Purpose: Create technical drawings from 3D models.
- Key Tools: Insert views, dimensions, annotations.
Related Posts-:
- How FreeCAD Becomes a Student’s Best Friend in Learning CAD
- Enhance Your Design Skills: Essential FreeCAD Tips for Better Creations
- Advantages of FreeCAD That Every FreeCAD user Must Know
4. FreeCAD Learning Resources-:
FreeCAD is a powerful, open-source 3D modeling software that offers immense potential for engineers, architects, designers, and hobbyists. Learning the intricacies of this software can be challenging without the right resources at hand. To master FreeCAD effectively, one must utilize a variety of learning materials such as tutorials, forums, documentation, and online courses. Websites like GitHub and the FreeCAD forum offer an extensive repository of user-generated content that can provide valuable insights into the software’s functionalities.
Additionally, official documentation provided by the FreeCAD developers offers a structured and comprehensive overview of all aspects of the software. Online platforms like Udemy or Coursera also offer specialized courses on FreeCAD for users looking to deepen their understanding further. By utilizing these diverse resources strategically, one can accelerate their learning process and unlock the full potential of FreeCAD within a professional setting.
a. FreeCAD Wiki-:
The FreeCAD Wiki is a comprehensive resource with tutorials, documentation, and examples. this wiki page covers all essential topic like Architecture and BIM, Modeling parts, Drafting and Sketching, Technical Drawings, FEM & CNC & 3D Printing.
If you’d like to contribute with writing wiki documentation and tutorials, see the general wiki guidelines in WikiPages, and read the Tutorial guidelines. Please notice the version of FreeCAD used in the tutorial as some tutorials may use an old version of the program. Although the general modelling process may still work, some tools may have changed.
b. YouTube Tutorials-:
- Search for FreeCAD tutorials on YouTube. Channels like Joko Engineeringhelp and MangoJelly Solutions offer excellent beginner-friendly content.
c. FreeCAD Forum-:
- Join the FreeCAD Forum to ask questions, share your work, and learn from others.
d. Online Courses-:
- Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and edX offer CAD courses that can complement your FreeCAD learning.
5. Tips for FreeCAD Beginners-:
As a beginner in FreeCAD, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the basic tools and functions of the software. Start by taking advantage of the various tutorials and documentation available online to gain a better understanding of how FreeCAD works. Practice creating simple 2D sketches and then move on to more complex 3D modeling projects. Pay attention to sketch constraints and dimensions to ensure accurate designs. Utilize keyboard shortcuts and customize your workspace to optimize efficiency.
Save your work frequently to prevent data loss and consider using version control systems for larger projects. Finally, don’t be afraid to ask for help or seek advice from the FreeCAD community forums when faced with challenges – learning from experienced users can greatly enhance your skills and proficiency in using this powerful open-source CAD software.
a. Start Simple-:
- Begin with basic shapes and gradually move to more complex models.
b. Use Constraints Wisely-:
- Apply constraints in the Sketcher Workbench to control the geometry of your sketches.
c. Leverage Parametric Design-:
- Use parameters and spreadsheets to create flexible models that can be easily modified.
d. Practice Regularly-:
- Consistent practice is key to mastering FreeCAD. Work on small projects to build your skills.
e. Explore Add-ons-:
- Use the Addon Manager to install additional workbenches and tools that can enhance your workflow.
6. Example Projects for Beginners-:
Here are some project ideas to practice and improve your FreeCAD skills:
a. Mechanical Parts
- Design gears, bolts, brackets, or other mechanical components.
b. Architectural Models
- Create models of buildings, houses, or interior layouts.
c. Product Design
- Design everyday objects like cups, phone stands, or lamps.
d. 3D Printing
- Create models for 3D printing, such as keychains, figurines, or functional parts.
e. Technical Drawings
- Practice creating technical drawings of your 3D models using the TechDraw Workbench.
7. Advanced Topics in FreeCAD-:
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, explore these advanced topics:
a. Python Scripting
- Automate tasks and create custom tools using Python.
b. Assembly Design
- Use add-ons like A2plus or Assembly4 to create and manage assemblies.
c. Simulation
- Use the FEM Workbench to perform structural and thermal simulations.
d. Rendering
- Use the Render Workbench to create photorealistic renderings of your models.
8. Join the FreeCAD Community-:
- Participate in the FreeCAD community to learn from others, share your work, and get feedback.
- Contribute to the FreeCAD project by reporting bugs, writing documentation, or developing features.
Conclusion-:
FreeCAD is a powerful and versatile tool that’s perfect for anyone looking to start 3D design without any cost. By following this guide, practicing regularly, and exploring the resources available, you’ll be well on your way to mastering FreeCAD and developing valuable skills for your future projects. Happy designing!
“Thank you for reading! If you found this article insightful and valuable, consider sharing it with your friends and followers on social media. Your share can help others discover this content too. Let’s spread knowledge together. Your support is greatly appreciated!”